Companies are investing huge funds into hiring experienced frontend developers or outsourcing; the average annual salary for frontend developers in the U.S. reaches over $110k and for good reason. From the design and layout to how products are displayed, the frontend plays a crucial role in how users navigate and engage with your storefront.
But what exactly is the frontend, and how does it work? In this guide, we'll introduce you to the basics of frontend in ecommerce, explaining its key components and why understanding it is essential for creating a user-friendly, high-converting online store.
What is frontend?
In ecommerce, the frontend is the so-called "client side" of the platform, the place where your customers interact with your brand – it's the digital storefront that shapes their shopping experience. It includes elements like the website's design, fonts, colors, images, and product pages.
Everything you see here is a storefront:
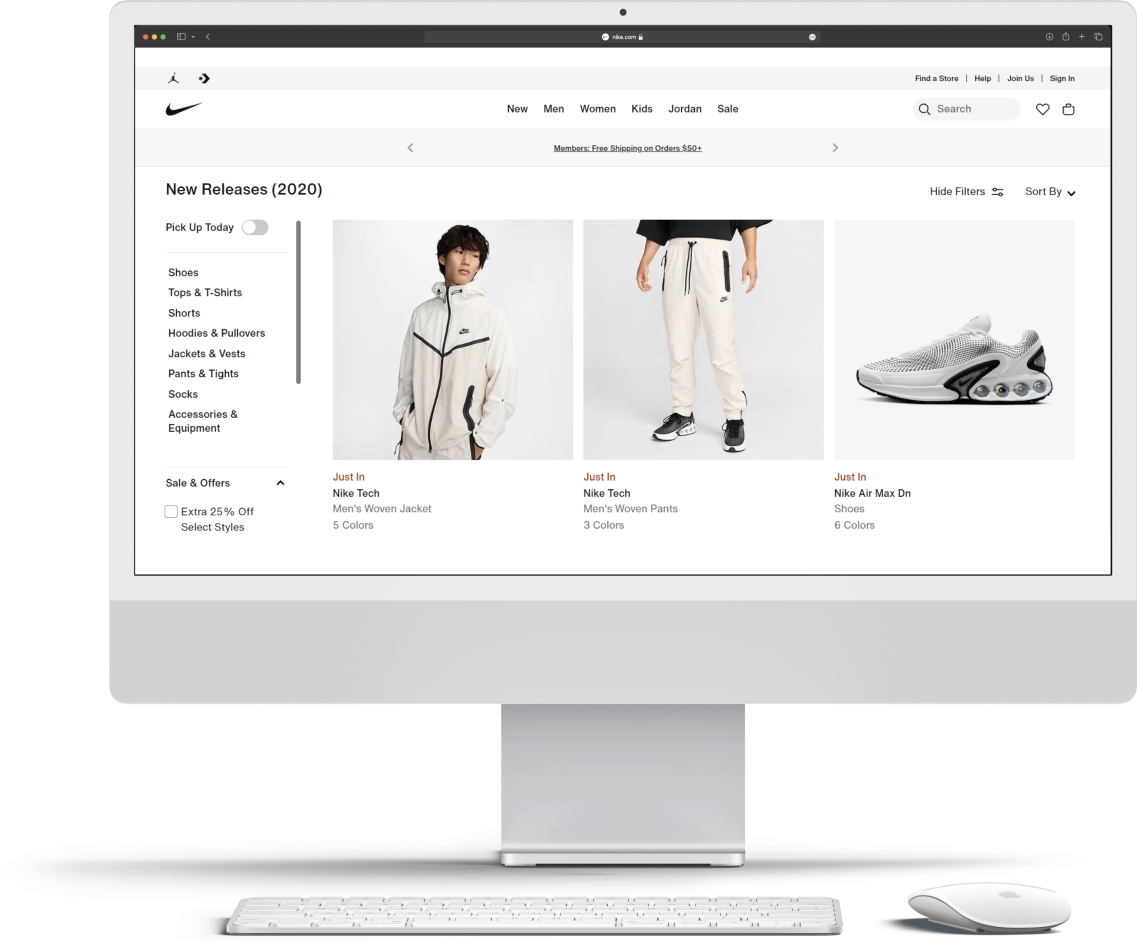
Just like a physical storefront of a brick-and-mortar store, it needs to be visually appealing and easy to navigate to maximize customer shopping experience.
Frontend development relies on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript programming languages to create an intuitive and visually attractive website. This is why user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are crucial components of frontend development; after all, it's the first thing people see and interact with when landing on a web store!
Why is frontend important for ecommerce?
In ecommerce, a smooth, visually appealing interface isn't just nice to have; it's a necessity for building trust and higher revenue. According to research, a good user interface increases the chances of conversion by as much as 200%.
By minimizing cart abandonment and maximizing user satisfaction, you’ll see a direct boost in sales and overall revenue. This isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about creating a compelling online store that converts visitors into buyers and drives long-term customer loyalty.
Read our ebook to learn more about the importance of frontend in ecommerce
Frontend vs. backend: The two pillars of ecommerce
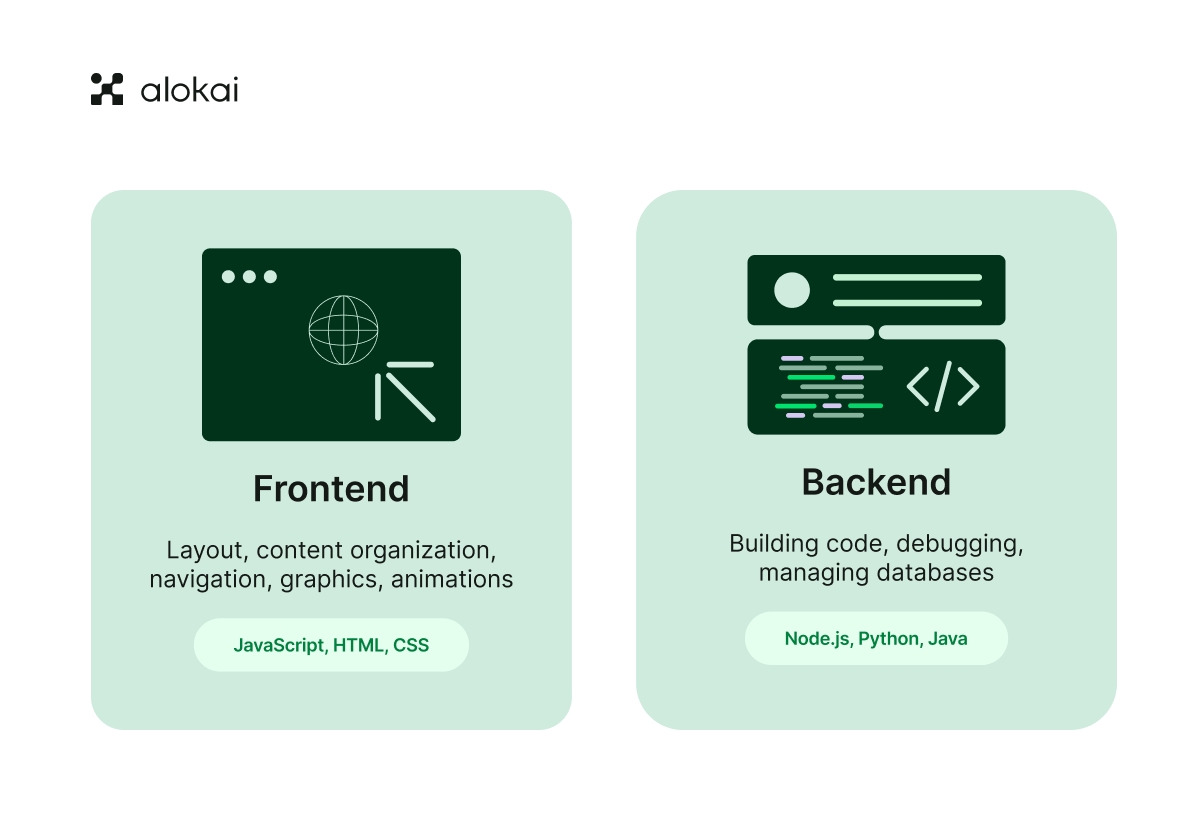
While the frontend of an ecommerce site is designed to create a functional and engaging customer experience, backend technologies are responsible for managing data like products, prices, customer information, and order details. The backend, or the server side of a website, makes the frontend function properly.
Some common backend technologies include PHP, Python, Java, and popular databases, like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
When it comes to web development, consider the backend as the staff working behind the scenes in a physical store – they ensure all products are available, the prices are accurate, and transactions are smooth and hassle-free. You need both the front- and the backend working harmoniously to deliver a seamless customer experience.
But we’ll focus on the frontend in this post.
3 key components of a winning frontend
Users today want seamless shopping experiences, with 74% expecting the same functionality and convenience they get from in-person or phone interactions. This is why when creating a well-functioning frontend for your website, you should keep in mind the 3 core elements of the presentation layer:
Web performance
User experience
Design
1. Web performance
One of the key elements of frontend is web performance. The first 5 seconds of page loading time are crucial for conversion rates. After those 5 seconds, conversion rates decrease by 4.42% with each additional second of loading. That's why performance leads to positive conversion optimization and revenue growth.
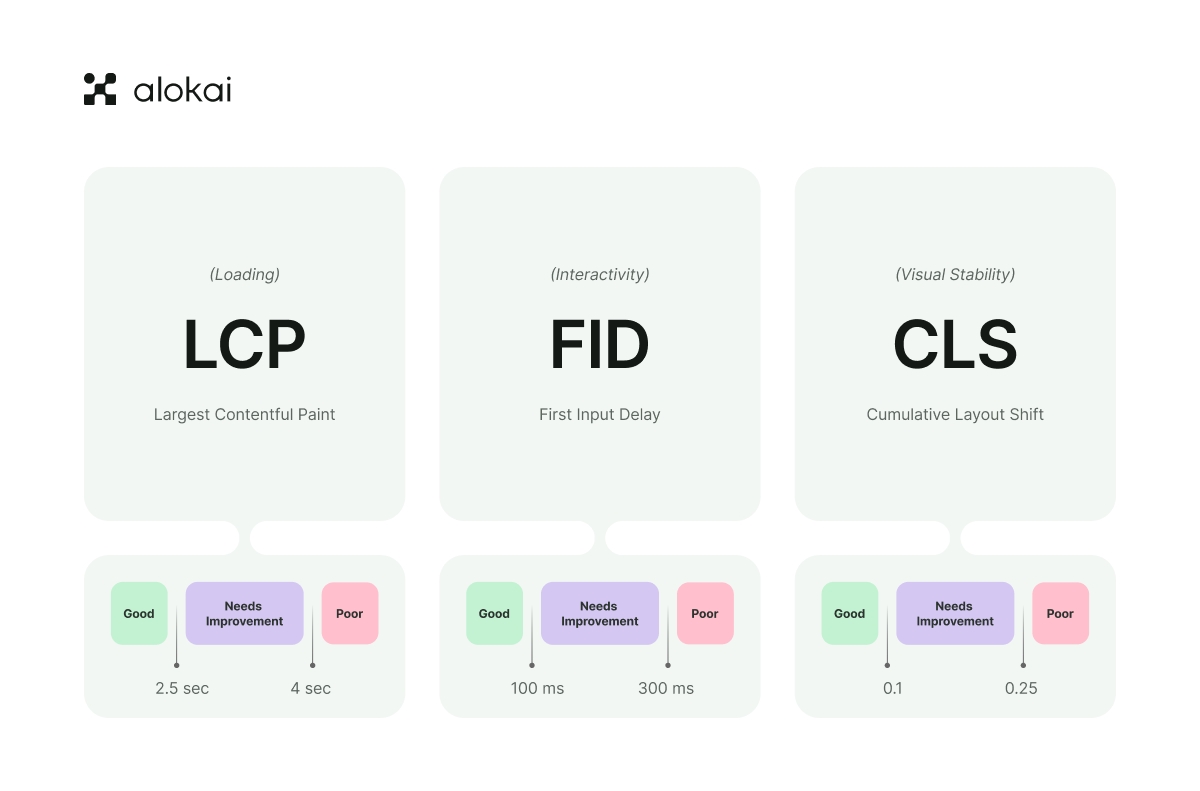
Excellent speed and website performance also translate to good SEO results. Search engines prioritize delivering a positive user experience, and website performance is a significant factor for the quality of that experience, which is measured by the Google Core Web Vitals. Since the 2021 update, Google has used page and image loading times as a core ranking element for websites.
2. User experience
UX focuses on how people use or interact with your product. It adopts the user perspective and answers the question, “How would a first-time customer approach this website?”.
UX design enhances user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided during the interaction.
There are many components of UX that need to be considered to ensure an excellent user experience. For example, let's take a look at the UX honeycomb made by Peter Morville:
This diagram sums up the foundation for a good UX, reminding us that a solid user experience comes from your design being:
Useful
Desirable
Accessible
Credible
Finable
Usable
Valuable
Remember, a pleasant user experience is what turns visitors into customers; data shows that 88% of users will not return to your website after a bad experience.
3. User interface
UI, or User Interface, is the store's overall look and feel. The colors, the typography, the buttons, the images – everything that makes up the visual aspects of a product is part of its user interface.
UI isn't just about aesthetics, though. A good UI design is intuitive and easy to navigate, allowing users to interact easily with your digital store. This is where companies focus on fleshing out their branding to ensure that both UI and UX work together to offer quality, usability, and brand identity.
UX, on the other hand, is about how a user interacts with a product. While design is a big part of it, UX is about the entire journey a user takes from the moment they land on a website.
Top frontend technologies for ecommerce
Choosing the right frontend technology for your ecommerce project can seem daunting with so many options on the table.
To provide more background, here's a quick rundown of the most popular frontend development technologies for you to choose from:
Angular.js is a structural framework for building JavaScript-heavy single-page-based web applications. It's used to change HTML from static to dynamic and extend its syntax to render the components of your website more clearly.
React.js is a JavaScript library for building fast and interactive user interfaces for web and mobile apps. It helps provide a cohesive user experience. This library is open-source and reusable component-based.
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework for building UIs. With Vue.js, you can start simple and then progressively add tools and features needed to build a complex web application. Vue.js allows incremental adoption, which makes it easy for developers to integrate it with other libraries.
Ecommerce frontend development: Monolith vs. headless solutions
Now that you know the definition of frontend and its role in enhancing customer experience, let's dig deeper into web building and the presentation layer world.
When it comes to building an ecommerce website, you have 2 options to choose from: a monolith legacy solution or a composable commercestack, starting with a storefront.
Let's find out the main difference between the two and why it's important to choose the method that serves your business needs best.
Option 1: Monolith legacy platforms (traditional approach)
Traditional legacy platforms (monolith solutions) had once been the only choice for building an online store. These platforms operate as all-in-one systems, where frontend and backend are heavily linked together in an intertwined architecture.
Legacy platforms are typically older systems that, while used to this day, are considered outdated compared to modern development practices.
Monolithic legacy platforms can face challenges like maintenance, updates, and scaling applications, especially compared to more modern modular architectures, such as microservices.
Benefits and challenges of monolith solutions
Traditional platforms have all the components needed for an ecommerce website within a single codebase. Companies can use traditional platforms to quickly deploy ecommerce websites and manage them without any problem by using templates.
Monolith, all-in-one platforms were designed to give full control of the system. This was and to some extent is a huge benefit but in modern ecommerce, control should go hand-in-hand with flexibility.
As the number of online stores grew and the competition became fierce, customers started to expect unique and smooth digital experiences. And that's when the challenges with monolithic systems began.
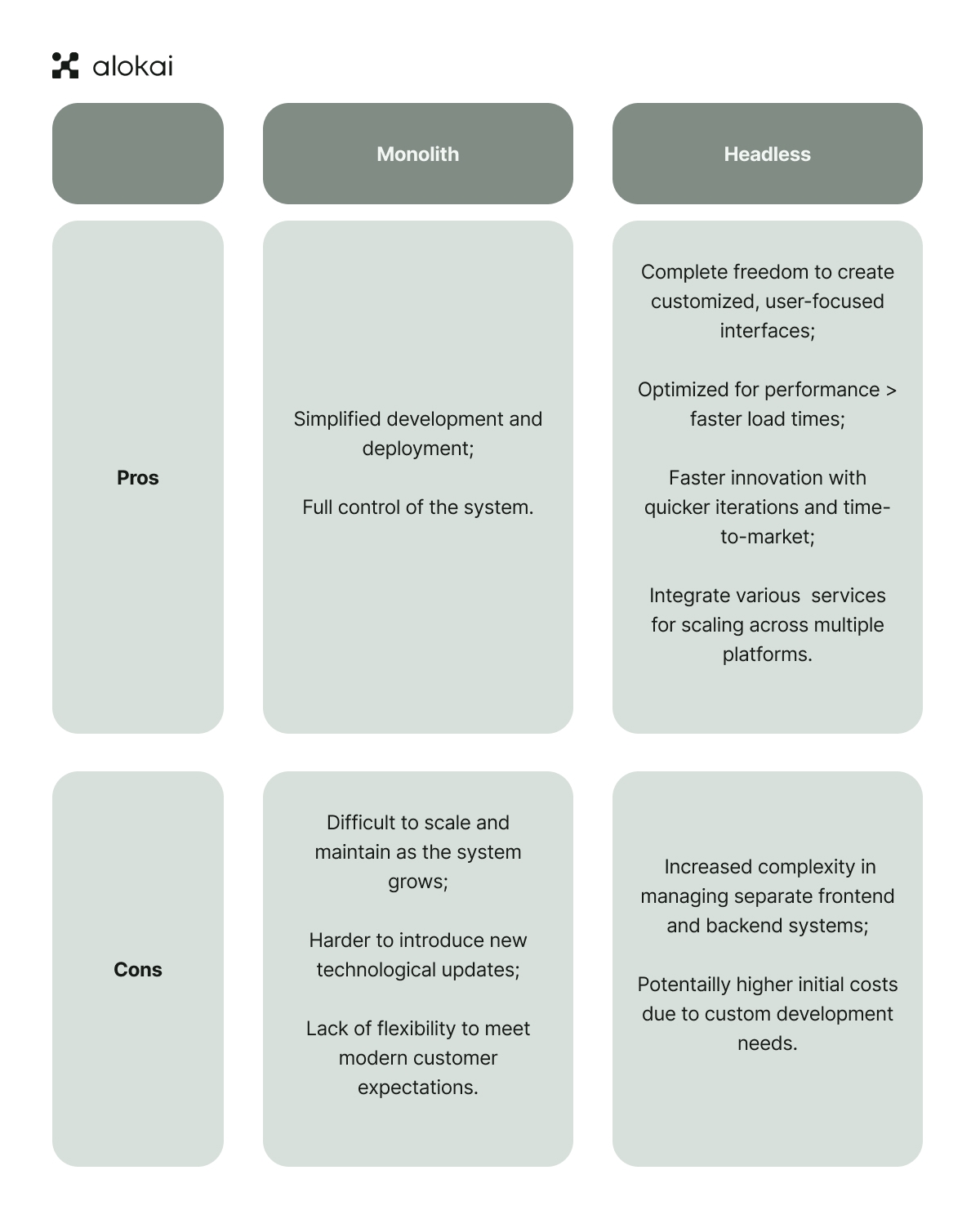
To be successful in any business, you have to be able to evolve. While monoliths give you perks such as simplified development and deployment, they're also a pain to scale and can be a real challenge in terms of introducing new technological updates.
Option 2: Headless architecture (new approach)
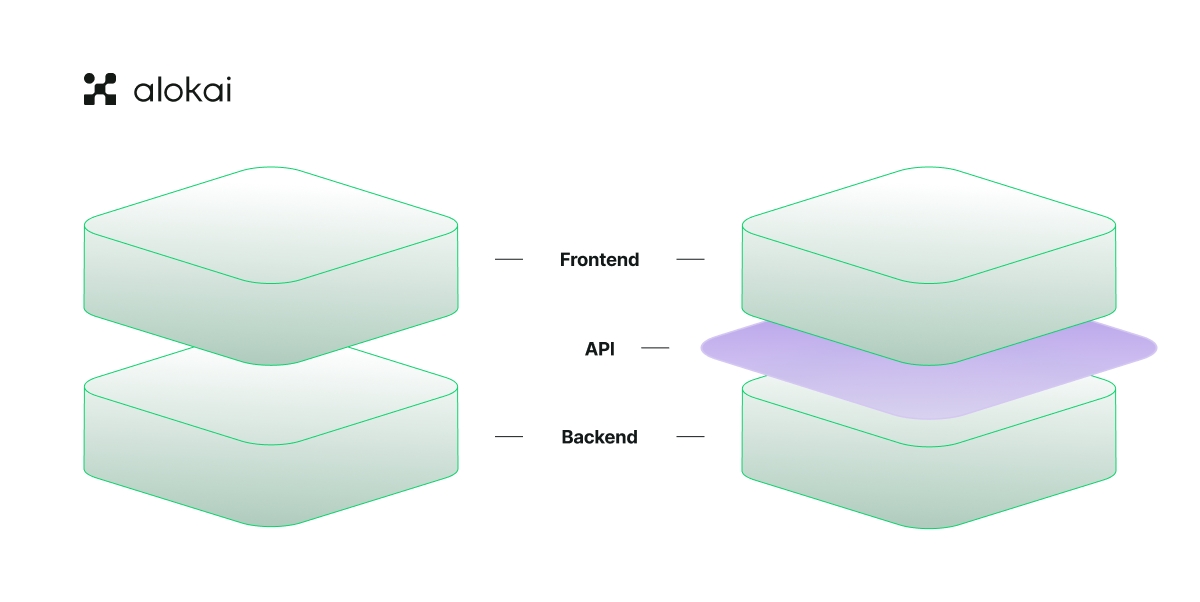
The headless frontend approach is based on the idea of separating the presentation layer (frontend) from the logic of the application (backend).
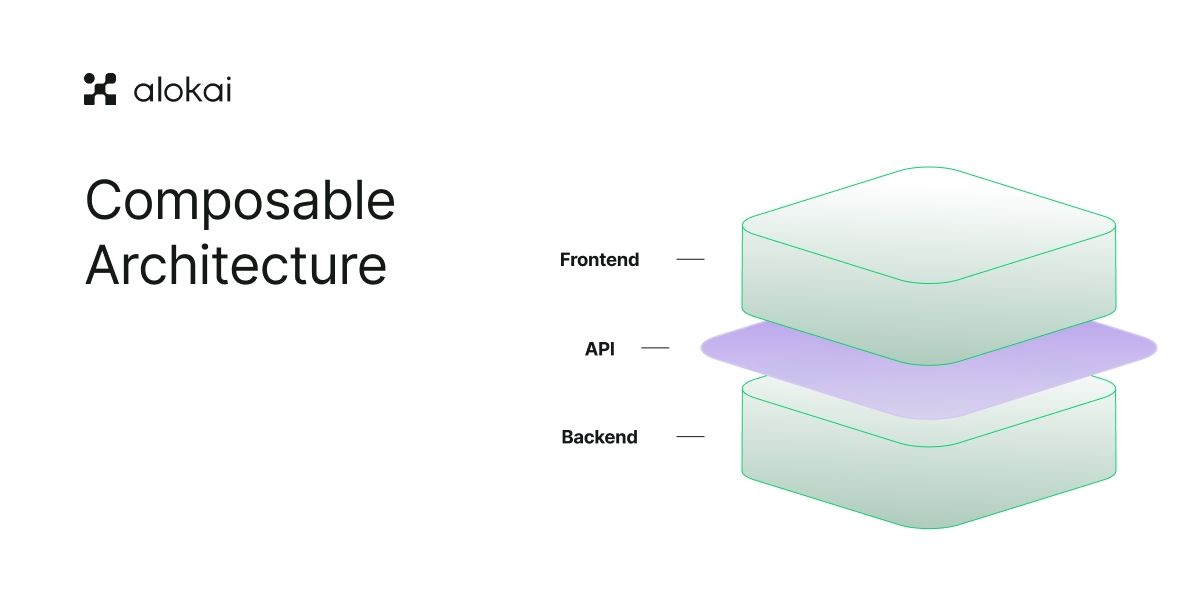
It allows to decouple frontend from the backend, providing freedom to add, replace, or update components as needed. Headless commerce is becoming a future-proof standard for the ecommerce industry as it gives the agility and flexibility of a startup to even the most mature enterprises.
Benefits and challenges of headless commerce solutions
Headless frontend gives developers complete freedom to create highly customized, user-focused interfaces, independent of backend constraints. This decoupling allows teams to optimize the frontend for performance, resulting in faster load times and smoother user experiences.
With headless, your developers can innovate faster, pushing out updates and new features without worrying about backend dependencies.
This means quicker iterations, faster time-to-market, and a better user experience that keeps your customers coming back. The flexibility to integrate various APIs and services allows businesses to scale across multiple platforms, delivering a consistent experience on web, mobile, and other channels.
Headless frontend also comes with some challenges, like the increased complexity of managing separate frontend and backend systems; it requires more advanced development skills to ensure seamless communication between the two layers. This decoupling can also lead to higher initial costs, as it demands custom development work.
However, in the long run, the benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles; if you want to keep up with the fast-paced ecommerce market, headless will give you the power to innovate, experiment with new technologies, and deliver a superior user experience.
Aligning your frontend with business goals
The frontend is what your website visitors see and interact with during their purchase process.
With a frontend-first approach, you can elevate customer experience by decoupling the frontend from the backend, allowing you to quickly update and optimize the UI without the need for complex system-wide changes. But how can you make sure that your frontend is doing its job well?
Prioritizing customer experience
Prioritizing customers should become one of the main goals of improving your ecommerce frontend. A high-quality, fast and mobile-first storefront is essential to deliver amazing customer experience and increase conversions and revenue. In fact, a staggering 80% of shoppers are more likely to make a purchase from a company that delivers personalized experiences tailored to their preferences.
Optimizing for fast load times
Users can't stand slow websites. And let's face it, it's true for all of us. The website should load fast and respond quickly (within 1-2 seconds). To put it into perspective, 1 to 5seconds of load time increases the bounce rate probability by a whopping 90%.
You can have a beautiful and engaging design, but if it's slow to load – you'll lose customers.
Implementing responsive design
In the omnichannel era, customers use various devices and operating systems on their buyer journey. According to Statista, the number of global mobile phone users will increase to 7,49 billion. The presentation layer of your website must ensure a smooth purchase process, regardless of the device a user might be using.
Here, take into consideration more than just desktop-vs-mobile differences. Consider tablets, desktops with different resolutions, smart TVs, etc.

Conclusion: Why frontend matters in ecommerce
Keeping up with the latest advancements isn't just the responsibility of your tech teams anymore – all the stakeholders need to be aware of new technologies that could be pivotal for your business strategies. Today's digital landscape is all about speed, flexibility, and user engagement – and that's exactly why businesses are choosing headless frontend.
And the best part? You don’t have to go big-bang and start a complete re-platforming project. Instead, you can start by replacing just the frontend and reaping the benefits much faster.
Frontend as a service: The future of ecommerce
To dive deeper into the question of how to properly build your website's frontend, you might consider Frontend-as-a-Service or FEaaS. Opting for headless commerce is a step to the future success of your online store paving the path to composable architecture, but you'll need the right approach to do that. That's where FEaaS comes into play.
FEaaS tools are separate from the commerce backend and focus solely on the frontend experience. It supplies ecommerce businesses with a one-stop-shop solution for creating performant storefronts from build to launch in one place, with one tool. Instead of hiring a development team or spending time on complex updates to your existing system, FEaaS does it all for you!
In a standard headless approach, you must handle a dozen microservices and the middleware. As a stellar example of a FEaaS solution,Alokai offers pre-built and ready-to-optimize building components, which allow you to customize the storefront instead of developing it from scratch.
Request a demo to discover how Alokai can help you create a fast, mobile-first frontend to drive conversions and revenue!
