Content modeling organizes your content by defining types, fields, and their relationships. This ensures consistency and scalability in your digital projects. In this article, learn what content modeling is, why it matters, and how to do it right.
Key takeaways
- Content modeling is a detailed process that defines the structure of digital content, aligning UX designers, editors, and developers to ensure cohesive content strategy and functionality.
- Well-crafted content models streamline content creation, ensure consistency and quality across channels, and support scalability as brands evolve.
- Effective content modeling practices involve creating modular structures, documenting relationships, involving cross-functional collaboration, and incorporating SEO considerations for enhanced visibility and performance.
Understanding content modeling
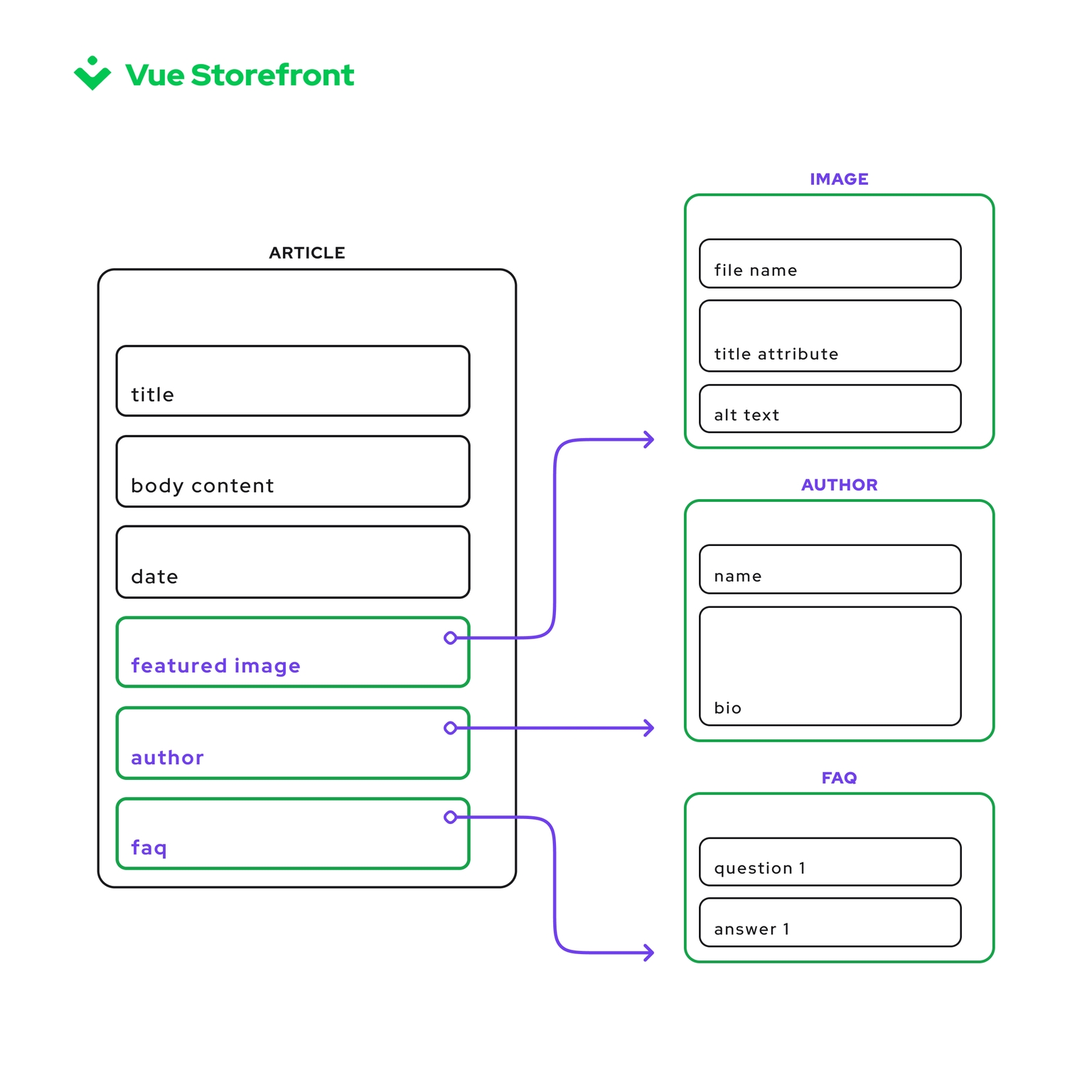
At its core, content modeling is the meticulous process of defining the structure of your content down to the finest detail. It’s the blueprint for your digital construction project, determining the types and fields of content that will populate your database. Think of fields as the building blocks for your structured content; they are the foundation upon which you can add various data types, bringing structure and organization to your web content. Content modeling is not a solitary task; it aligns the efforts of UX designers, editors, and developers, ensuring that the content strategy envisioned is a dream and a reality. It directs APIs on the content to deliver to end applications, and while it’s a tool primarily wielded internally by the project team, its effects are far-reaching.
Crucially, a content model is not static; it evolves with the project, adapting to the changing landscape of digital content needs. In platforms like Contentful, the content model is tailored to the pieces of content, liberating it from the constraints of predefined models and allowing a more natural fit for developers and editors. This tailored approach ensures that the model serves its purpose well, accommodating all content types and guiding both the creation of content and its eventual presentation.
The Importance of content modeling
Diving deeper into the world of content modeling reveals its undeniable significance. This process is a compass for collaboration, guiding different roles to work together seamlessly toward a shared vision. It shapes a clear blueprint, eliminating the need for constant back-and-forth, and enables teams to focus on what they do best: creating a content model, designing, and developing. The efficiency in content creation echoes through the entire workflow, as a well-crafted content model provides a framework that streamlines processes, saving precious time and resources.
Beyond efficiency, the benefits of content modeling are evident as it acts as the guardian of quality and consistency. It ensures that the voice and image of a brand are uniform across all channels, instilling confidence in the audience and supporting scalability as the brand grows and evolves. Moreover, content models act as a roadmap, documenting the present and the future of content, enabling managers to revamp outdated material and address any issues within the content management system (CMS).
Key elements of a content model
Understanding the anatomy of a content model is essential for anyone looking to harness its power. At the heart of the model are:
- Content types: the assets that bring value and purpose, like articles or product listings
- Content items: the actual content created, just like cookies shaped by a cookie cutter, each made from a content type
- Fields: including text and relation fields, the essential content type’s elements in modeling content, providing the structure needed for various data types such as headlines, dates, and body text for a news article page.
Attributes describe a content type, giving it depth and meaning, while relationships map out the interconnectedness of different content types within the model. Content modules, on the other hand, are the compartments that help organize large content models into manageable segments, easing the complexity that often accompanies extensive content modeling endeavors.
Steps to create a content model

It begins with clearly understanding and aligning the purpose with the business’s objectives. It’s about knowing the content you’re working with and the intricate details that must be communicated throughout the project. This requires thorough research to grasp the audience’s preferences and a cross-functional brainstorming session to identify the main content types. Engaging in the content modeling process early lays the groundwork for an efficient content strategy and provides better-informed insights that are invaluable as the project progresses.
Even in the early stages of a project, tools like Post-it notes can prove useful for in-person collaboration, serving as a simple yet effective method for creating modular content models. The goal is to consider the content workflow and team dynamics, determining what type of information will be repeatable or reusable, which in turn will inform the structure for each content template.
Identifying content types
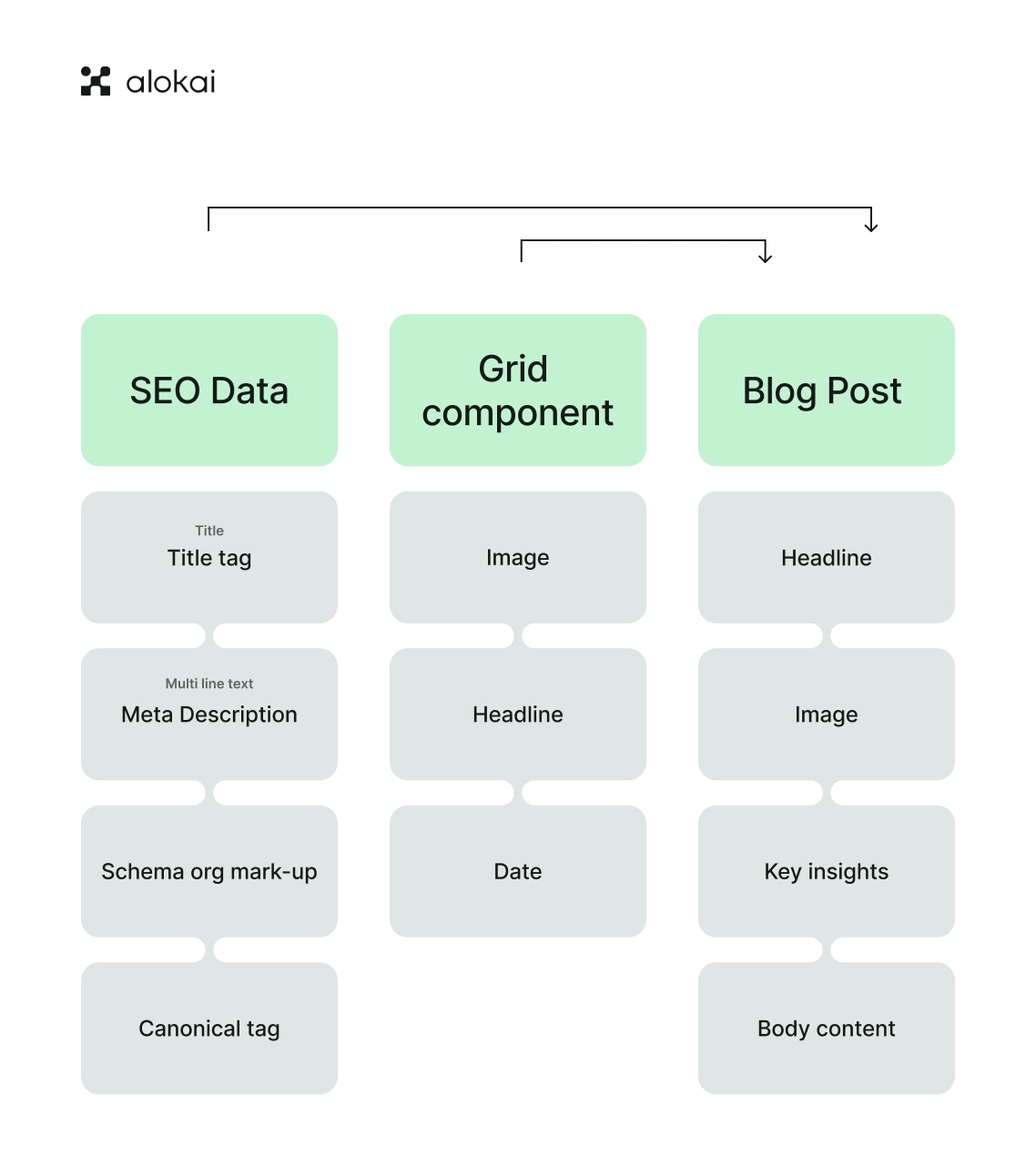
The quest to identify distinct content types is akin to unraveling a tapestry to discover the patterns woven within. It’s about abstracting the kinds of created content and looking for commonalities that inform the new content types. Reviewing existing content to spot these patterns and mapping out the user journey to determine the necessary content types at each stage is crucial.
Segmenting content based on audience personas ensures that each type addresses specific user needs, aligning the content with the intended audience experience. Analyzing content requirements thoroughly from the outset is vital, as it informs the key attributes and fields for each content type, paving the way for a content model that is both comprehensive and manageable.
Ultimately, the components of content modeling touch upon various aspects like products, categories, and elements such as blog posts, each requiring careful consideration to ensure they serve their purpose effectively. An approach to content modeling that considers these aspects, including creating a well-structured blog post, is essential for success. By employing strategies for content modeling, you can optimize your content to serve its intended purpose better.
Defining content attributes
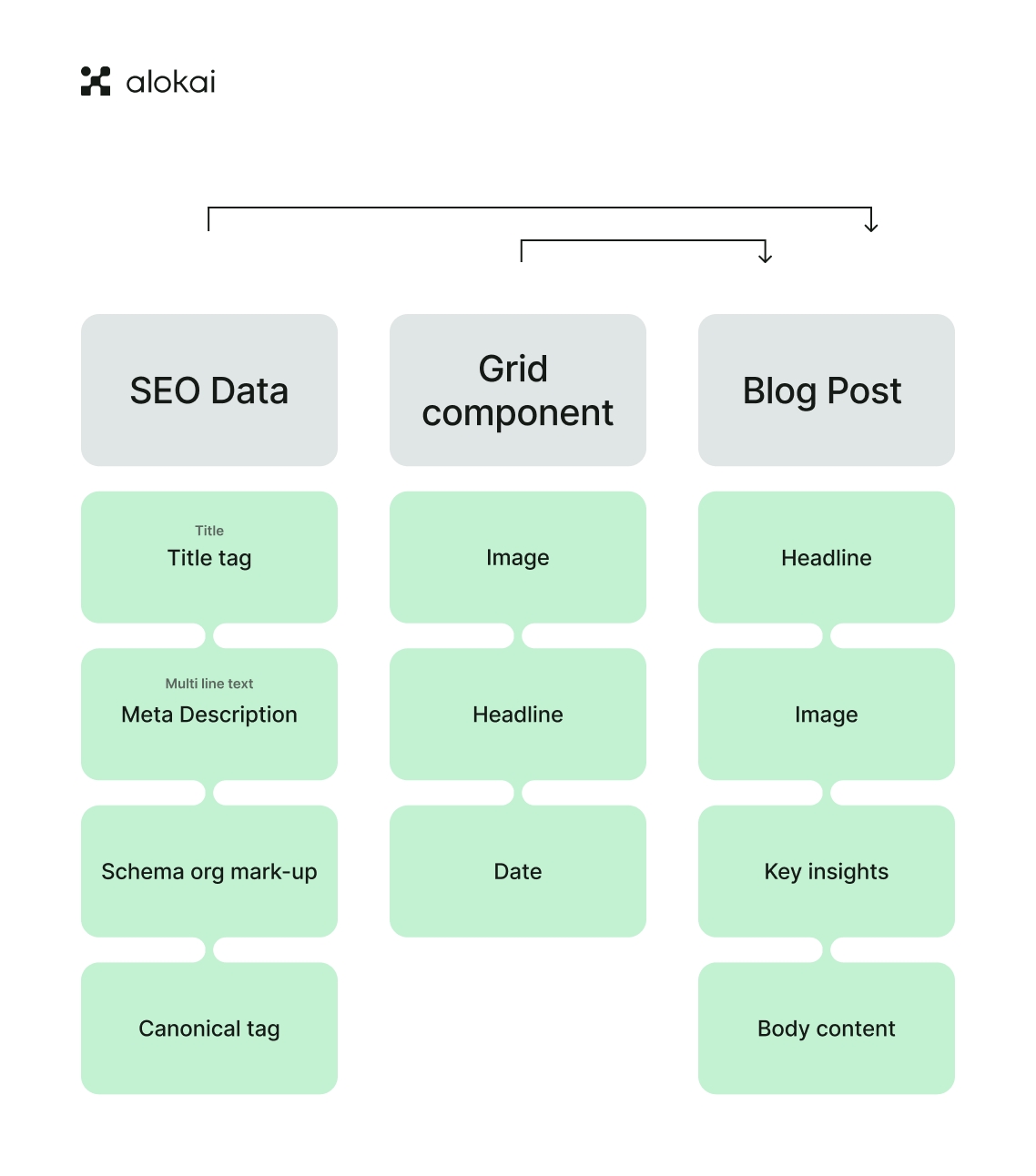
As we delve into defining content attributes, we essentially paint the finer details that bring each content type to life. It involves identifying the visible content, metadata, and relationships that will form the backbone of our content types. Specifying which attributes are mandatory and which are optional is a step towards consistency, ensuring a uniform experience across all content items. Attributes that enhance accessibility, such as alternative text for images, are not to be overlooked, as they contribute to a more inclusive digital environment.
Identifying repeatable groups of attributes within a content item facilitates the creation of content items with specific characteristics, streamlining the content creation and management process. This level of detail helps content creators produce content that not only meets the business needs but also resonates with the audience.
Establishing relationships

Establishing relationships in a content model involves documenting the intricate web of connections between content types. This ensures that content items can reference or embed other content types as needed, creating a rich and dynamic content experience. Documenting these relationships helps stakeholders understand how content should be structured and presented, supporting a coherent strategy that aligns with the project goals.
Planning for hierarchical relationships, such as parent-child structures, is particularly important when dealing with complex content organization. It allows for a logical taxonomy that is both intuitive and scalable. These relationships are the threads that bind the content, creating a cohesive narrative that unfolds across different platforms and touchpoints.
Best practices for effective content modeling
As we navigate the content modeling landscape, certain best practices emerge as beacons guiding us toward creating models that are not only effective but also resilient. Embracing modularity is key, as it increases the adaptability of content elements, allowing them to be reused and repurposed easily. Flexibility in content models encourages the creation of content that can adjust to the evolving demands of the digital space, ensuring the content team’s job remains efficient.
Establishing a content lifecycle process that includes regular reviews and updates is essential to keep content relevant and engaging. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Start with detailed information and create small, modular content models that can be connected through relationships.
- Ensure that complexity is managed without sacrificing consistency and reusability.
- Balance modularity with presentation needs to ensure that content models are easy to understand and practical to use.
By following these steps, you can create a content lifecycle process to help you maintain high-quality content over time.
Modular vs. presentation-centric models
In content modeling, the balance between modularity and presentation-centric approaches is akin to walking a tightrope. On the one hand, modular content models offer the allure of reusability and flexibility, allowing content to be adapted across various presentation layers with relative ease. This flexibility is particularly valuable in headless commerce, where the need to serve content across multiple platforms is paramount. Divorcing page builder mentality and embracing a more modular approach can lead to greater adaptability and success in today’s digital landscape.
On the other hand, presentation-centric content models are designed with a particular display in mind, which can lead to limitations when repurposing content for different contexts. The key is to strike a balance, ensuring that content models are not fractured into tiny modules that become complex to manage nor rigidly tied to specific presentation layers, such as the presentation layer that inhibit flexibility.
Documentation and validation
The content modeling craft is incomplete without the twin pillars of documentation and validation. Detailed content model documents for each content type, specifying its attributes and metadata, serve as the compass that guides the entire team, from content creators to developers. Comprehensive documentation, including detailed definitions, ensures consistency and clarity as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle.
Storing the content model in various formats, such as data schemas, spreadsheets, and diagrams, maximizes accessibility for all stakeholders, ensuring that everyone can interact with it effectively. Validating the content model with stakeholders is akin to a litmus test, confirming that it meets the diverse needs and expectations of those involved.
Iterative design and feedback
The beauty of iterative design in content modeling is that it mirrors the natural process of evolution, adapting and improving with each feedback loop. Regular input from team members can unearth issues early on, allowing for timely adjustments that refine the model into a robust framework. Collaboration plays a pivotal role here, with tech teams and business analysts working together to decide on the best approach, ensuring that the model is effective but also logical and intuitive.
Embracing reusability by creating shared content components offers several benefits:
- Streamlines workflows
- Fosters collaboration among different teams
- Leads to a model that is both versatile and user-friendly
- Ensures that the content model remains relevant and effective, even as the digital landscape continues to shift and evolve.
Content modeling in headless CMS
Content modeling takes on a new dimension in the context of a headless CMS. The content model formally represents content types and their interrelationships, serving as the blueprint for a flexible and dynamic content management system. Embracing reusability and scalability is especially important in headless CMS, where the content needs to be future-friendly and adaptable to various end applications.
Defining content types, their relationships, and structures in a headless CMS allows for more flexible content management, with the CMS acting as a repository for all content elements. In this environment, content template structures, called entries, are the basic units, each with its associated fields. Examples of headless CMS platforms, such as Contentstack, Contentful, and Sanity, illustrate the diversity and capabilities of these systems in the current digital ecosystem.
Using reference fields
Reference fields in a headless CMS are the glue that binds different content types together, creating a network of relationships that enrich the content experience. These fields allow users to link one content model to another, such as connecting a product model to its category, enabling intricate content structures that can be easily navigated.
The benefits of using reference fields include:
- Reusability of content entries, allowing a single entry to be utilized across multiple content types
- Maximizing the value of each piece of content
- Configuring reference fields to allow multiple references, enabling a content type to link to various entries of a target content type
- Fostering a rich and interconnected content ecosystem
Managing field settings and validations
Within the headless CMS, managing field settings involves configuring the appearance and validation options for each type of field, which is crucial for maintaining a consistent and user-friendly content entry process. Implementing these configurations can shape how content creators interact with the CMS, influencing the efficiency and accuracy of content entry. For instance, the appearance tab in Contentful’s content modeling determines how fields appear within the entry editor, aiding creators in inputting and selecting values more easily.
Field settings also encompass options such as hiding fields during editing to reduce clutter while still making their content available in the API response or, conversely, disabling fields in the API response to prevent them from being served to the end application. Validation settings are equally important, allowing content architects to set specific requirements for content entry, such as character limits and predefined values, and ensuring that reference fields link to the correct content type, thus safeguarding the integrity and usability of the content.
SEO considerations in content modeling
SEO considerations are woven into the fabric of content modeling, potentially significantly elevating a brand’s digital presence. A well-structured content model facilitates an efficient content strategy and bolsters internal linking, enhancing both the user experience and the site’s ranking in search engine results. By ensuring that key pages are easily accessible and linked from relevant content, content models become an indispensable ally in the quest for SEO optimization.
Creating a global field for SEO metadata, including tags, is a recommended best practice. It centralizes SEO efforts and maintains consistency across all content types, laying a strong foundation for future SEO endeavors. This strategic integration of SEO within content modeling transforms the content from simply being discoverable to prominently visible in the digital landscape.
SEO-friendly content types
To construct SEO-friendly content types, infuse them with SEO-specific fields, ensuring that elements like meta descriptions and keywords become integral parts of the content’s architecture. These attributes improve search engine visibility and enhance the likelihood of content being discovered and ranked favorably. Incorporating headless SEO best practices, such as schema markups, further refines content types, making them more attractive to search engines and more likely to appear in rich snippets and other enhanced search results.
An SEO-friendly content model considers all aspects of content, from blog posts to landing pages, ensuring that each piece is crafted with visibility in mind. By doing so, content types become powerful tools in a brand’s SEO arsenal, enabling content to perform well in search results and drive organic traffic to the site.
Collaboration with SEO specialists
In the intricate dance of content modeling, SEO specialists are essential partners, bringing their expertise to ensure that content structures align with SEO goals. This collaboration is pivotal, as it guarantees that the content model supports better visibility in search results, making it a key step in the journey toward SEO success. Involving SEO specialists early in the content modeling process allows for integrating important keywords and SEO strategies that resonate with search engines and audiences alike.
The collaborative process should be intuitive for SEO professionals, with the content modeling process structured in a way that is logical and easily navigable. By doing so, the content model becomes a shared language between content creators and SEO experts, enabling them to work together to create and distribute content that not only meets the brand’s narrative but also excels in the digital marketplace.
Common challenges and solutions in content modeling
Content modeling is not devoid of challenges, ranging from managing complex content structures to ensuring cross-team collaboration. These challenges can significantly impact the efficiency and success of content strategies and require thoughtful solutions. Some common challenges include:
- Managing complex content structures
- Ensuring cross-team collaboration
- Lack of buy-in from the entire company
- Difficulties in adjusting the content model later on
To overcome these challenges, having a shared vision and understanding from the outset and involving all relevant teams in the content modeling process is important, which is a critical step.
Creating a content type for every new instance or adding new fields for existing data can also result in a convoluted and challenging-to-manage model. To address these challenges, it’s crucial to prioritize reusability and avoid redundancy, ensuring each content attribute is unique and serves a purpose.
To maintain a strong and coherent content strategy, consider the following:
- Prioritize reusability and avoid redundancy in content creation
- Develop a content governance model to support consistency and quality
- Regularly review and update content attributes to ensure they serve a purpose
By following these guidelines, you can create and distribute online a more efficient and effective content management system that is most appropriate for your needs.
By addressing these and other challenges head-on, teams can create content models that are efficient consistent and of the highest quality.
Handling complex content structures
Handling complex content structures demands a focus on building models that are both reusable and manageable. Avoiding the creation of unique content types for minor variations and instead using established rules and restrictions prevents the model from becoming bloated and unwieldy. By adopting slice variations and incorporating structured data, teams can provide flexibility without adding complexity, enabling content creators to maintain a single component while offering different visual styles, thus promoting an efficient workflow around creating quality content.
It’s imperative to focus on creating a logical taxonomy that simplifies content organization and enhances the overall content strategy. This approach allows the content team to interact with complex content structures more effectively, ensuring that the content remains clear, structured, and easy to navigate, regardless of its complexity.
Ensuring cross-team collaboration
Cross-team collaboration is the linchpin in the successful implementation of a content model, requiring open communication and the involvement of diverse team members. From UX designers to developers, marketers to SEO specialists, each brings a unique perspective that enriches the content model. Establishing touchpoints for planning and implementation helps maintain alignment across teams, ensuring that agreed-upon outcomes are met and that the content model serves the needs of the entire project.
By involving SEO specialists in the process, content models are optimized for search engines from the beginning, setting the foundation for a strong SEO strategy supporting the brand’s digital presence. This collaborative effort not only modernizes workflows but also saves time and resources, enabling teams to serve up relevant and optimized content for search engines, meeting the demands of today’s digital landscape.
Summary
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it’s clear that the ultimate goal of content modeling is to craft a structured, adaptable, and efficient framework for managing digital content. From defining content types and attributes to establishing relationships and considering SEO, each step in the content modeling process contributes to creating a robust, future-proof content strategy. Embracing best practices, such as modularity, documentation, and iterative design, ensures that content models are effective and resilient in the face of an ever-evolving digital ecosystem.
Let this guide serve as your beacon, illuminating the path to a well-structured content model that meets business objectives, enhances user experience, and drives SEO performance. With the knowledge and strategies shared herein, you are now equipped to tackle the challenges of content modeling, collaborate effectively across teams, and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines. It’s time to take the reins and transform your content into a structured masterpiece that stands the test of time.
